WHAT IS INFRARED?
Infrared radiation, also known as infrared light or infrared waves, is a form of energy with frequencies and wavelengths just below the visible light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Infrared was discovered by William Hershel in the 19th century while conducting experiments that measured the temperature difference between colors in the visible light spectrum. Herschel chose the name infrared, which is Latin for "below," because he believed they were located "below the red light" in the spectrum. Although the human eye cannot see infrared waves, we can feel infrared energy in the form of heat. Any object with a temperature above 0°K will radiate infrared energy; However, the two most obvious sources of infrared are fire and the sun.
The electromagnetic spectrum

USE OF INFRARED
Electrical infrared heat is used in many industrial and commercial process heat applications as a way to heat materials quickly and efficiently by penetrating directly through air to the target. These IR waves hit the target directly without heating the surrounding air, as would occur in a convection oven. IR energy is converted to heat when it impacts and is absorbed by an opaque object.
Electrical infrared is generated by sending electricity through infrared emitters, such as infrared lamps or quartz tubes, and other resistance means. The emitter becomes very hot and emits invisible infrared heat waves. As the temperature of the heat source increases, infrared energy production increases to the fourth power of the emitter temperature. Therefore, infrared heaters/emitters are extremely efficient, due to this law of physics (reference Stefan-Boltzmann Law), do not require heating the surrounding air and have relatively instantaneous on/off control.
TYPES OF IR WAVES
There are three types of infrared waves, each with its own characteristics.
- short wave
- medium wave
- long wave
Classifying an infrared emitter as long, medium, or short wave allows you to quickly determine the approximate wavelength range measured in microns. When infrared is applied to an object, the energy is absorbed, reflected, or transmitted. The spectral characteristics and energy output of infrared are important factors to consider in determining which wavelength will produce the most effective and energy-efficient heating process.
Infrared energy absorption diagram.
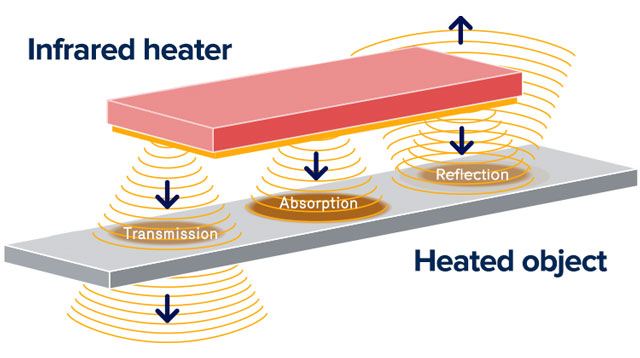
Some thermal processing applications are forgiving and can work well with long, medium, or short wave infrared. However, there are certain applications that require a more tedious combination for a successful heating process.
Choosing the right wavelength can make a huge difference in the overall efficiency, accuracy and speed of the process. Additionally, emissivity, color sensitivity, and absorption are characteristics that determine which infrared wavelength is needed to achieve the best results.

